HBGI Q1 2025: Multifamily Growth in Smaller Markets
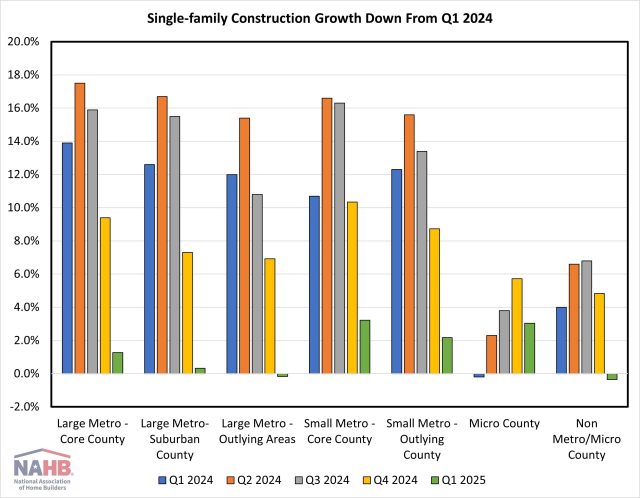
Jesse Wade2025-06-03T14:20:31-05:00Single-family construction growth slowed substantially across all markets in the first quarter of 2025, according to the Home Building Geography Index (HBGI). Multifamily construction growth remained negative in the largest markets but reported significant expansion in lower population density areas. The HBGI tracks single-family and multifamily permits across seven population density delineated geographies in the United States. Single-Family Among the HBGI geographies, the highest growth in the first quarter of 2025 was registered in small metro core counties, which increased 3.2% year-over-year on a four-quarter moving average basis (4QMA). The market with the largest decline in growth between the fourth quarter and first quarter was large metro core counties, which saw its four-quarter moving average growth rate fall from 9.4% to 1.3% (-8.1 pp). Two geographies, large metro outlying areas and non metro/micro counties, reported declines in the first quarter, down 0.2% and 0.4% respectively. In terms of market share, single-family construction took place primarily in small metro core county areas, representing 29.2% of single-family construction. The smallest single-family construction market remained non metro/micro county areas, with a 4.2% market share. Single-family construction market share have been stable since the first quarter of 2024, with the largest gain being 0.4 percentage points in small metro core counties over the year. Multifamily Multifamily construction expanded 33.2% in large metro outlying areas in the first quarter, the highest growth (4QMA) since the second quarter of 2022 when this geography grew 71.8%. Growth was present in three other geographies, with micro counties up 29.3%, small metro outlying counties up 18.5%, and non metro/micro counties up 3.7%. Because of the notable increase in multifamily construction occurring in smaller markets, market shares have shifted over the past two years. Large metro core counties, where a plurality of construction takes place, saw a 4.8 percentage point drop in market share between Q1 of 2024 and 2025. The largest construction gains have been in low population density areas, with the combined market share for small metro outlying counites, micro counties and non metro/micro counties growing 2.2 percentage points from 7.8% to 10.0% between Q1 2024 and 2025. The first quarter of 2025 HBGI data along with an interactive HBGI map can be found at http://nahb.org/hbgi. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.