The Fed Pause Continues
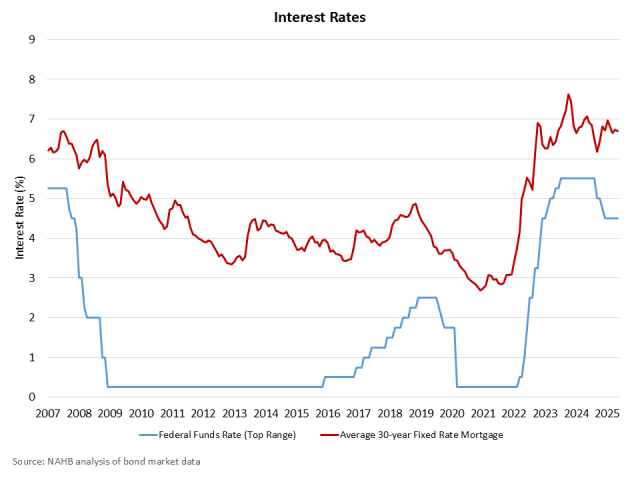
Robert Dietz2025-06-18T15:17:06-05:00Reflecting most forecasters’ expectations for the June FOMC meeting, the Federal Reserve continued its post-2024 pause for federal funds rate cuts, retaining a target rate of 4.5% to 4.25%. The pause comes after a 100 basis point series of reductions in late 2024. Despite these cuts, mortgage rates have remained in the high 6% range. The Fed also held unchanged its ongoing quantitative tightening program, which is more strongly focused on balance sheet reduction for mortgage-backed securities (MBS). The Fed reaffirmed its policy commitment to achieve maximum employment and reduce inflation to a two percent target rate. During the 2025 policy pause, the Fed remains data dependent in a “wait and see” mode for developments in areas like tariff policy. Chair Powell noted that we learn more about tariffs later this summer. NAHB’s forecast incorporates two rate cuts from the Fed for 2025, one in the third quarter and one in the fourth quarter. The Fed noted that economic activity continues at a “solid pace,” however swings in imports affected the first quarter GDP data. The central bank also stated that the unemployment rate remains low and inflation remains “somewhat elevated.” I would note that the primary driver of this elevated inflation is ongoing high rates of shelter inflation, which reflect significant, underlying increases for residential construction costs for the post-covid period. During his press conference, Chair Powell cited that the housing market suffers from both long-run and short-run issues, involving affordability and a [structural] housing shortage. In prior comments to Congress, Powell has noted that home builders face a perfect storm of challenges from both the demand- and supply-sides of the market. The Federal Reserve also published an update for its Summary of Economic Projections (SEP). Compared to its prior March projections, the Fed reduced its 2025 GDP forecast from 1.7% to 1.4% (year-over-year rate from the fourth quarter). During his press conference, Chair Powell linked policy uncertainty as a complicating factor for economic growth. Additionally in the SEP, the Fed slightly increased its 2025 forecast for the unemployment rate in the fourth quarter from 4.4% to 4.5%. The central bank also increased its core PCE inflation projection for the final quarter of the year from 2.8% to 3.1%. During his press conference, Chair Powell noted that economic forecasters cited tariff policy as a contributing factor for a higher than expected level of inflation for 2025. He specifically projected that a measurable amount of inflation will arrive to the economy this summer. There is some debate among economists whether tariffs would have just a one-time impact on the aggregate price level, which would not be inflation pressure felt over a sustained period of time, or would in fact be a factor increasing inflation as a series of price increases. Looking forward to future monetary policy, the “dot plot” projections of the SEP leave the Fed forecasting two rate cuts in 2025, followed by just one reduction in 2026 and one more cut in 2027. This projection removes one rate cute from both 2026 and 2027 compared to the March dot plot, although the Fed continues to point to 3% as the long-run, terminal rate for the federal funds rate. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.