Housing’s Share of the Economy Grows Higher to Start the Year
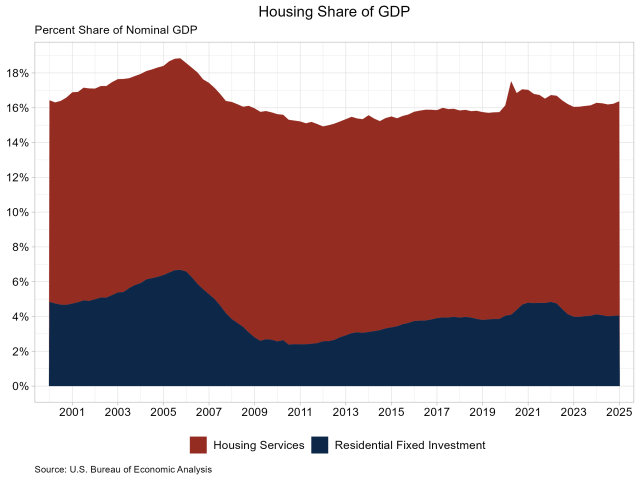
Jesse Wade2025-05-01T08:22:40-05:00Housing’s share of the economy grew to 16.4% in the first quarter of 2025, according to the advance estimate of GDP produced by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. This is the highest reading since the third quarter of 2022 and is up 0.2 percentage points from the fourth quarter of 2024. The more cyclical home building and remodeling component – residential fixed investment (RFI) – was 4.1% of GDP, up from 4.0% in the previous quarter. The second component – housing services – was 12.3% of GDP, up from 12.2% in the previous quarter. The graph below stacks the nominal shares for housing services and RFI, resulting in housing’s total share of the economy. Housing service growth is much less volatile when compared to RFI due to the cyclical nature of RFI. Historically, RFI has averaged roughly 5% of GDP, while housing services have averaged between 12% and 13%, for a combined 17% to 18% of GDP. These shares tend to vary over the business cycle. However, the housing share of GDP lagged during the post-Great Recession period due to underbuilding, particularly for the single-family sector. In the first quarter, RFI added 5 basis points to the headline GDP growth rate, marking the second straight quarter of positive contributions. RFI was 4.1% of the economy, recording a $1.216 trillion seasonally adjusted annual pace. Among the two segments of RFI, residential structures rose 1.2% while residential equipment rose 5.5%. Breaking down the components of residential structures, single-family structure RFI grew 5.9%, while multifamily investment fell 11.5%. RFI for multifamily structures has contracted for seven consecutive quarters. Permanent site structure RFI, which is made up of single-family and multifamily RFI, grew 1.2%. Other structures RFI rose 0.6% in the first quarter, down from 11.4% the previous period. The second impact of housing on GDP is the measure of housing services. Similar to the RFI, housing services consumption can be broken out into two components. The first component, housing, includes gross rents paid by renters, owners’ imputed rent (an estimate of how much it would cost to rent owner-occupied units), rental value of farm dwellings, and group housing. The inclusion of owners’ imputed rent is necessary from a national income accounting approach, because without this measure, increases in homeownership would result in declines in GDP. The second component, household utilities, is composed of consumption expenditures on water supply, sanitation, electricity, and gas. For the first quarter, housing services represented 12.4% of the economy or $3.691 trillion on a seasonally adjusted annual basis. Housing services expenditures grew 3.4% at an annual rate in the first quarter and contributed 41 basis points to GDP growth. Real personal consumption expenditures for housing grew 1.3%, while household utilities expenditures grew 18.7%. Real personal expenditures for natural gas services grew 53.1% in the first quarter, as residential consumption of natural gas recorded its highest monthly level since January 2014, at 1.035 trillion cubic feet in January 2025. Through the first two months of 2025, residential households consumed 1.833 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, higher than the 1.582 trillion in 2024 and 1.498 trillion in 2023. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.