Declines for Custom Home Building
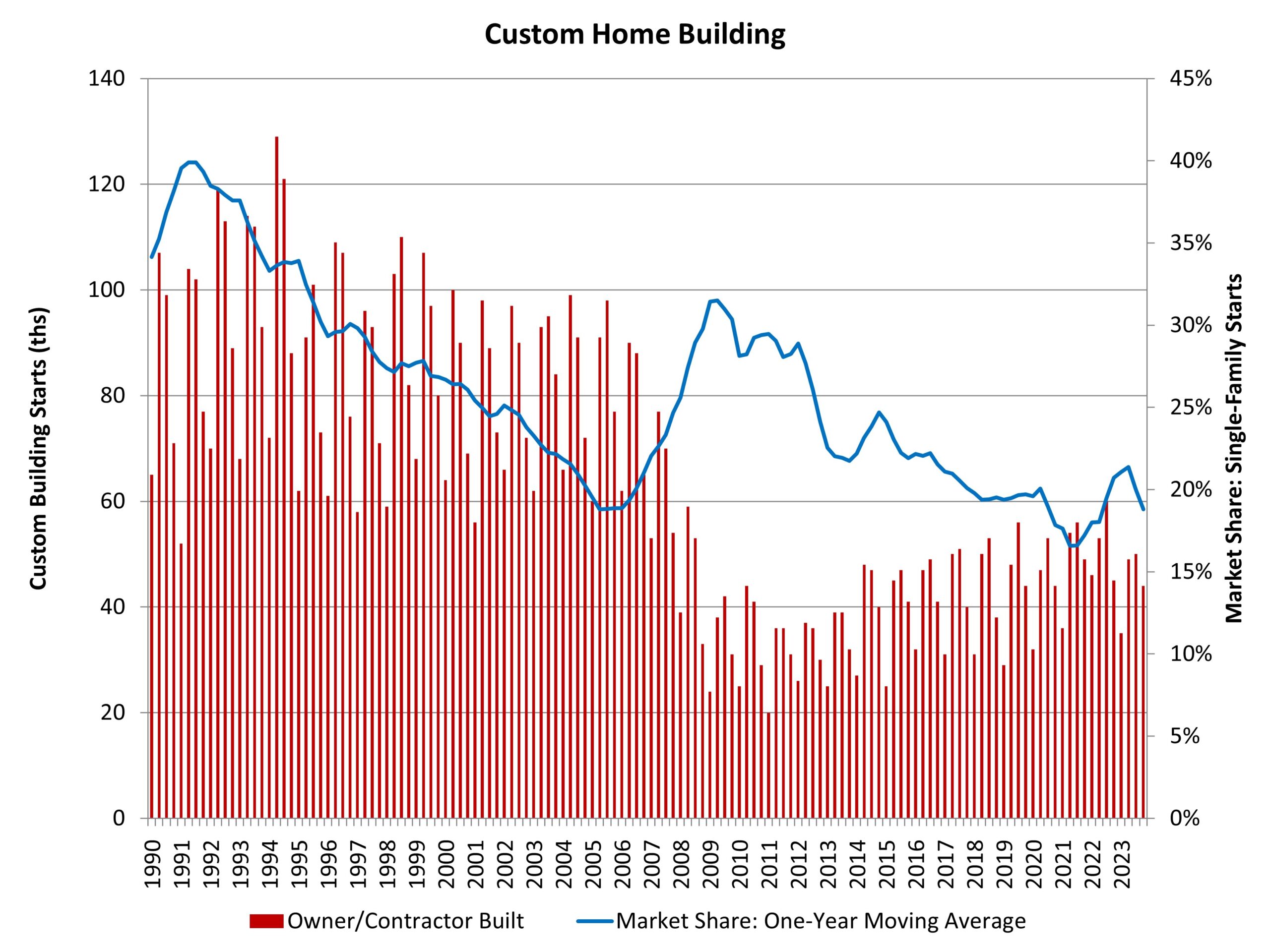
Robert Dietz2024-02-20T08:18:40-06:00By Robert Dietz on February 20, 2024 • NAHB’s analysis of Census Data from the Quarterly Starts and Completions by Purpose and Design survey indicates a slowing market for custom home building after a recent gain in market share. There were 44,000 total custom building starts during the fourth quarter of 2023. This marks a more than 2% decline compared to the fourth quarter of 2022, consistent with weakness experienced throughout the home building sector. Over the last four quarters, custom housing starts totaled 178,000 homes, a nearly 13% decline compared to the prior four quarter total (204,000). After share declines due to a rise in spec building in the wake of the pandemic, the market share for custom homes increased until recently. As measured on a one-year moving average, the market share of custom home building, in terms of total single-family starts, has fallen back to just under 19%. This is down from a prior cycle peak of 31.5% set during the second quarter of 2009. Note that this definition of custom home building does not include homes intended for sale, so the analysis in this post uses a narrow definition of the sector. It represents home construction undertaken on a contract basis for which the builder does not hold tax basis in the structure during construction. ‹ Strong Quarter for Single-Family Built-for-Rent ConstructionTags: custom, custom building, economics, home building, housing, single-family