Solid Job Growth in June
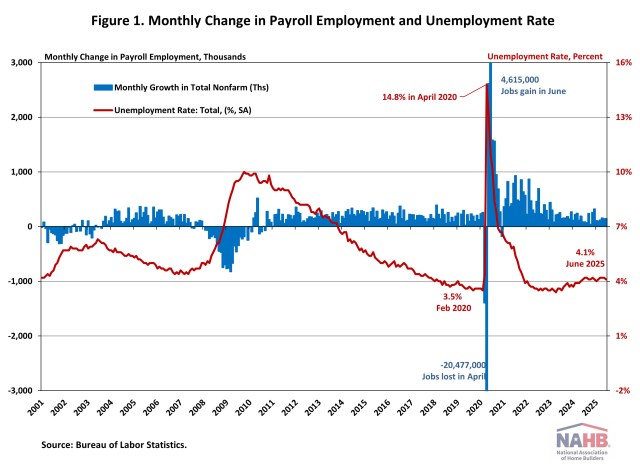
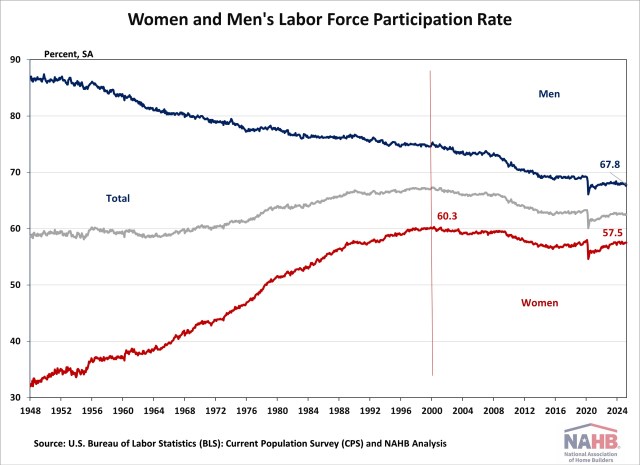
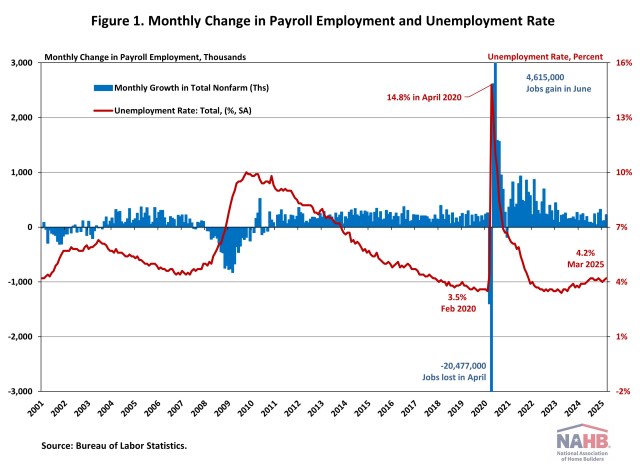
Jing Fu2025-07-03T11:17:21-05:00The U.S. labor market continued to show resilience in June, with steady job gains led by state/local government and health care sectors. The unemployment rate edged down to 4.1%, signaling ongoing strength in hiring despite persistent economic uncertainty. However, there were some indications that the headline number overstated the health of the labor market, including slowing wage growth and much of the job gains concentrated in state/local government. In June, wage growth slowed. Year-over-year, wages grew at a 3.7% rate, down 0.1 percentage point from the previous month. Wage growth has been outpacing inflation for nearly two years, which typically occurs as productivity increases. National Employment According to the Employment Situation Summary reported by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), total nonfarm payroll employment rose by 147,000 in June, following an upwardly revised increase of 144,000 jobs in May. Since January 2021, the U.S. job market has seen 54 consecutive months of job growth, making the third-longest period of employment expansion on record. In 2025, monthly employment growth has averaged 124,000, compared with the 168,000 monthly average gain for 2024. The estimates for the previous two months were revised upward. The monthly change in total nonfarm payroll employment for April was revised up by 11,000 from +147,000 to +158,000, while the change for May was revised up by 30,000 from +139,000 to +144,000. Combined, the revisions were 16,000 higher than previously reported. The unemployment rate declined to 4.1% in June. The June decrease in the unemployment rate reflected the decrease in the number of persons unemployed (-222,000) and the increase in the number of persons employed (93,000). Meanwhile, the labor force participation rate—the proportion of the population either looking for a job or already holding a job—decreased by one percentage point to 62.3%. This remains below its pre-pandemic level of 63.3% recorded at the beginning of 2020. Among individuals aged 25 to 54, the participation rate rose by one percentage point to 83.5%. However, the rate for the prime working-age group (25 to 54) has been trending downward since reaching a peak of 83.9% last summer. In June, job gains occurred in state/local government and health care. State/local government posted a large 80,000 combined net job gain for June, while the health care sector added 39,000 jobs, with the largest increases occurring in hospitals and in nursing and residential care facilities. In contrast, the federal government continued to experience job losses, shedding 7,000 positions in June and a total of 69,000 since January 2025, reflecting the effects of government cutbacks. The BLS notes that “employees on paid leave or receiving ongoing severance pay are counted as employed in the establishment survey.” Construction Employment Employment in the overall construction sector rose by 15,000 in June, following an upwardly revised gain of 6,000 in May. While residential construction gained 5,500 jobs, non-residential construction employment added 9,200 jobs during the month. Residential construction employment now stands at 3.3 million in June, broken down as 959,000 builders and 2.4 million residential specialty trade contractors. The six-month moving average of job gains for residential construction was -1,833 a month, reflecting the three months of job losses recorded over the past six months, specifically in January, March, and May of 2025. Over the last 12 months, home builders and remodelers experienced a net loss of 1,400 jobs, marking the second annual decline since September 2020. Since the low point following the Great Recession, residential construction has gained 1,360,600 positions. In June, the unemployment rate for construction workers declined to 3.5% on a seasonally adjusted basis. The unemployment rate for construction workers has remained at a relatively lower level, after reaching 15.3% in April 2020 due to the housing demand impact of the COVID-19 pandemic. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.