Inflation Up Slightly in May
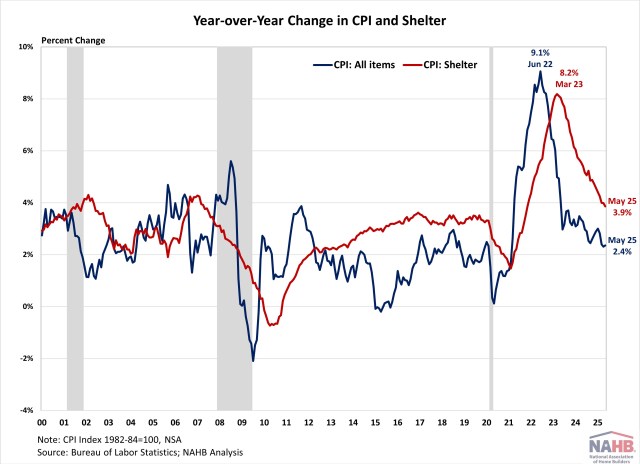
Fan-Yu Kuo2025-06-11T10:16:58-05:00Despite inflationary pressure from tariffs, inflation in May rose slightly but came in softer than expected. The Consumer Price Index increased from 2.3% in April to 2.4% in May year-over-year, according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics’ report. While this report reflected consumer prices after Liberation Day, it showed little sign of tariff impact as most reciprocal tariffs were paused for 90 days and many businesses had frontloaded imports ahead of tariffs. This preemptive action contributed a drag on the first quarter GDP growth. Additionally, the Bureau of Labor Statistics reduced its CPI collection sample starting in April due to staffing shortages, raising potential data quality concerns. Given these factors, it may be too early to gauge the impact of tariffs, as tariff-driven price increases have not yet materialized. Meanwhile, housing inflation remains elevated, though it continues to ease gradually. During the past twelve months, on a non-seasonally adjusted basis, the Consumer Price Index rose by 2.4% in May. Excluding the volatile food and energy components, the “core” CPI increased by 2.8% over the past twelve months. A large portion of the “core” CPI is the housing shelter index, which increased 3.9% over the year, the lowest reading since November 2021. Meanwhile, the component index of food rose by 2.9%, and the energy component index fell by 3.5%. On a monthly basis, the CPI rose by 0.1% in May (seasonally adjusted), after a 0.2% increase in April. The “core” CPI increased by 0.1% in May. The price index for a broad set of energy sources fell by 1.0% in May, with increases in electricity (0.9%) and fuel oil (0.9%) offset by declines in gasoline (-2.6%) and natural gas (-1.0%). Meanwhile, the food index rose by 0.3%, after a 0.1% decrease in April. Both food away from home and food at home increased by 0.3%. The index for shelter (+0.3%) was the largest contributor to the monthly increase in all items index. Other top contributors that rose in May include indexes for medical care (+0.3%), motor vehicle insurance (+0.7%), household furnishings and operations (+0.3%), personal care (+0.5%), as well as education (+0.3%). Meanwhile, the index for airline fares (-2.7%) and used cars and trucks (-0.5%) were among the few major indexes that decreased over the month. The index for shelter makes up more than 40% of the “core” CPI, rising by 0.3% in May, following an increase of 0.3% in April. The index for owners’ equivalent rent (OER) rose by 0.3% and index for rent of primary residence (RPR) increased by 0.2% over the month. Despite the moderation, shelter costs remained the largest contributors to headline inflation. While the Fed rate cuts could ease some housing market pressure, its ability to address rising housing costs is limited, as these increases are driven by a lack of affordable supply and increasing development costs. Tight monetary policy actually hurts housing supply by increasing AD&C financing cost. This can be seen on the graph below, as shelter costs continued rising despite Fed policy tightening in 2022. Additional housing supply is the primary solution to tame housing inflation and overall inflation. This emphasizes why the cost of construction, including the cost of building materials, matters not just for housing but also the inflation outlook and the path of future monetary policy. NAHB constructs a “real” rent index to indicate whether inflation in rents is faster or slower than core inflation. It provides insight into the supply and demand conditions for rental housing. When inflation in rents is rising faster than core inflation, the real rent index rises and vice versa. The real rent index is calculated by dividing the price index for rent by the core CPI (to exclude the volatile food and energy components). In May, the Real Rent Index rose by 0.1%. Over the first five months of 2025, the average monthly growth rate held steady at 0.1%, unchanged from the same period in 2024. Discover more from Eye On Housing Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.